Revision [23034]
This is an old revision of OctaveBildverarbeitung made by ToBo on 2016-03-12 01:52:16.
Basic Image Processing with Octave
GNU Octave Version 3.0.5
Operating System: Linux 2.6.31-21-generic #59-Ubuntu SMP Wed Mar 24 07:28:56 UTC 2010 i686
This are very simple image processing examples. I might by good to get basic understanding of how you can manipulate images.
Some basics first!
How to load an image? Download one of my images (kanu2010.jpg) or use your own. Do not take big images for testing save time waiting for images being processed.
Check image size
whos I ans = 375 500 3
Width, Length, number of colors.
View images
show.m
figure(1);
subplot(1,2,1);
image(I/4);
axis off equal tight;
title('Original');
subplot(1,2,2);
image(J/4);
axis off equal tight;
title('Bearbeitet');
subplot(1,2,1);
image(I/4);
axis off equal tight;
title('Original');
subplot(1,2,2);
image(J/4);
axis off equal tight;
title('Bearbeitet');
Bearbeitet is German and it means processed. this page was previously in German.
Better alternative to imshow():
show.m
figure(1);
subplot(1,2,1);
imshow(I/4);
title('Original');
subplot(1,2,2);
imshow(J/4);
title('Bearbeitet');
subplot(1,2,1);
imshow(I/4);
title('Original');
subplot(1,2,2);
imshow(J/4);
title('Bearbeitet');
Image histogram
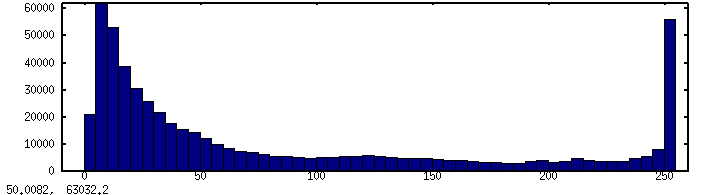
Try to interprate the histogramm looking at the image. How many bright and dark pixels can you see in the image? Is the image oversaturated (intensity 255) somewhere?
Now, lets start with some very basic examples.
Example 1
Reduce brightness by -50 stepsIncrease contrast by +30 %
J=(I-50)*1.3;

Example 2
Reduce green channel by 50 %

Example 3
Calculate gray image
J=fix(I); % uint8 in real umwandel
J(:,:,1)=(J(:,:,1)+J(:,:,2)+J(:,:,3))/3; % Mittelwert aus allen Kanälen
J(:,:,2)=J(:,:,1); % Kanal kopieren
J(:,:,3)=J(:,:,1); % Kanal kopieren
J(:,:,1)=(J(:,:,1)+J(:,:,2)+J(:,:,3))/3; % Mittelwert aus allen Kanälen
J(:,:,2)=J(:,:,1); % Kanal kopieren
J(:,:,3)=J(:,:,1); % Kanal kopieren

Example 4
Copy green channel to red channel. Green and blue channels stay untouched.

Example 5
Exchange green and blue channels. ;-)

Example 6
Blur image using a simple moving average low-pass filter. Moving average is not the best choice but lets keep it simple.

Example 7
Detect edges and add the edges to the original image, giving the image more sharpeness.
You should see the difference clearly on the water. If not just increase the factor 1.5 to 3 ore more
We reuse the low-pass filter from above to get a low-pass filtered iamge. And then we take the original (I) and substract the low-pass filtered image (I-J). This give us a high-pass filtered image (H). The high-pass filtered image represents the edges.
Finally, we add the high-pass filtered image multiplied by a factor (H) to the original image (I).

Example 8
Generate a black and white image. Just two colors: white and black!
Load another image.
First generate a gray image.
J=fix(I); % uint8 in real umwandeln
J(:,:,1)=(J(:,:,1)+J(:,:,2)+J(:,:,3))/3; % Mittelwert aus allen Kanälen
J(:,:,2)=J(:,:,1); % Kanal kopieren
J(:,:,3)=J(:,:,1); % Kanal kopieren
J(:,:,1)=(J(:,:,1)+J(:,:,2)+J(:,:,3))/3; % Mittelwert aus allen Kanälen
J(:,:,2)=J(:,:,1); % Kanal kopieren
J(:,:,3)=J(:,:,1); % Kanal kopieren
Now, calculate a threshold and generate the black and white image.

Calculate the percentage of white pixels.
White pixels: 78 %
Example 9
Generate a three color image using only black, red and yellow colors.
J(:,:,1)=((K(:,:,1)+77)>128)*255;show;
J(:,:,2)=((K(:,:,2)+60)>128)*255;show;
J(:,:,3)=((K(:,:,3)+47)>128)*255;show;
J(:,:,2)=((K(:,:,2)+60)>128)*255;show;
J(:,:,3)=((K(:,:,3)+47)>128)*255;show;

Example 10
Special effects ;.)

Example 11
Edge detector according to an algorithm by Rachid Deriche.

Now, it's your turn trying your own manipulations. I am sure you did already. ;-)
Siehe auch